 “Other ancillary techniques”).
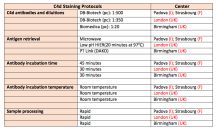
C4d staining protocols
used in centers involved in the web-tutorial preparation are described.
Pitfalls
Unlike other solid organ transplants, as the kidney, where the immunohistochemistry
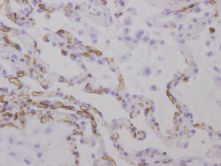
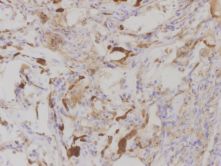
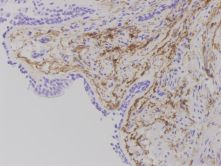
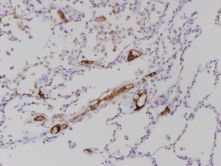
and the role of C4d is more standardized and accepted, C4d staining in the lung frequently
showed non specific patterns in areas of fibrin deposition, elastic tissue,
and intravascular serum (Figures 2,3,4).
Serum staining can be particularly difficult to interpret because it appears as
dense plugs within capillaries and often thick staining around the capillaries.
“Other ancillary techniques”).
C4d staining protocols
used in centers involved in the web-tutorial preparation are described.
Pitfalls
Unlike other solid organ transplants, as the kidney, where the immunohistochemistry
and the role of C4d is more standardized and accepted, C4d staining in the lung frequently
showed non specific patterns in areas of fibrin deposition, elastic tissue,
and intravascular serum (Figures 2,3,4).
Serum staining can be particularly difficult to interpret because it appears as
dense plugs within capillaries and often thick staining around the capillaries.In this case a careful search of this feature is mandatory to distinguish it from true endothelial positivity and a repetition of immunostaining is recommended. C4d staining should not be evaluated in the vessels of bronchial submucosa, in venules and arterioles. M. Angeles Montero (Pathologist, RBH, London, UK) References :
1. Wallace WD, Li N, Andersen CB, Arrossi AV, Askar M, Berry GJ, DeNicola MM, Neil DA, Pavlisko EN, Reed EF, Remmelink M, Sam Weigt S, Weynand B, Zhang JQ, Budev MM, Farver CF. Banff Study of Pathologic Changes in Lung Allograft Biopsy Specimens With Donor-Specific Antibodies. J Heart Lung Transplant; 2015; 1–9.
2. Yousem S, Zeevi A. The histopathology of lung allograft dysfunction associated with the development of donor-specific HLA alloantibodies. Am J Surg Pathol; 2012; 36(7):987–92.
3. Witt CA, Gaut JP, Yusen RD, Byers DE, Iuppa JA, Bennett Bain K, Alexander Patterson G, Mohanakumar T, Trulock EP, Hachem RR. Acute antibody-mediated rejection after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2013 Oct;32(10):1034-40.
4. DeNicola MM, Weight SS, Belperio JA, Reed EF, Ross DJ, Wallace WD. Pathologic findings in lung allografts with anti-HLA antibodies. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2013;32(3):326–32.
5. Berry GJ, Burke MM, Andersen C, Bruneval P, Fedrigo M, Fishbein MC, Goddard M, Hammond EH, Leone O, Marboe C, Miller D, Neil D, Rassl D, Revelo MP, Rice A, Rene Rodriguez E, Stewart S, Tan CD, Winters GL, West L, Mehra MR, Angelini A. The 2013 International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Working Formulation for the standardization of nomenclature in the pathologic diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection in heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2013 Dec;32(12):1147-62.
6. Li F, Wei J, Valenzuela NM, Lai C, Zhang Q, Gjertson D, Fishbein MC, Kobashigawa JA, Deng M, Reed EF. Phosphorylated S6 kinase and S6 ribosomal protein are diagnostic markers of antibody-mediated rejection in heart allografts. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015 Apr;34(4):580-7.